The
Best
Thumb Brace Has Certain Features
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Reasons to wear a thumb brace
- Does your thumb brace need a "spica"?
- Most important feature: COMFORT
- Best thumb brace for Sprains
- Best thumb brace for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- Summary
- FAQs
- About
Overview
Are you searching for the best thumb brace to relieve your hand and wrist pain? Before buying one, it’s important to understand what a thumb brace actually does—and how it differs from a standard wrist brace.
A wrist brace is designed to support the entire wrist and hand, restricting motion to reduce strain on the median nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. By limiting wrist flexion and extension, it helps decrease nerve compression and inflammation.
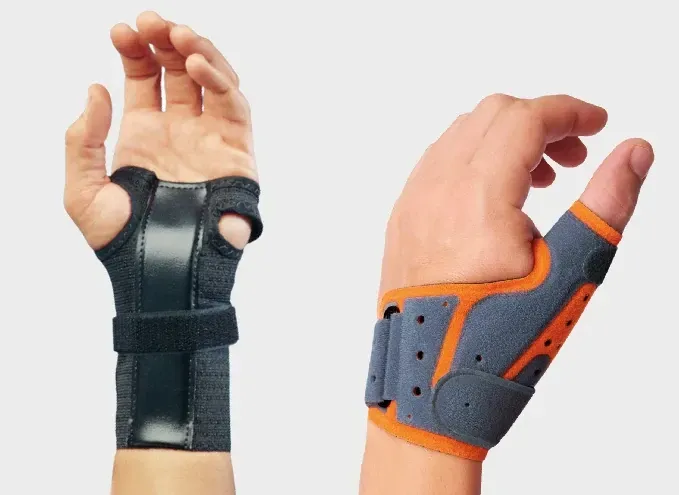
A thumb brace, on the other hand, focuses support primarily on the thumb joint (the carpometacarpal or CMC joint). It stabilizes the thumb during gripping, pinching, or texting, which helps when pain stems from thumb tendinitis, De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, or thumb arthritis. However, most thumb braces provide little or no restriction to wrist movement—making them less effective for treating true carpal tunnel syndrome.
When shopping for a brace, knowing which condition you’re targeting is essential. The right brace can relieve pressure, improve alignment, and prevent further irritation.
In this article, we’ll explain when a thumb brace is useful for carpal tunnel symptoms, which features matter most, and how to choose one that offers real therapeutic benefit.
Reasons to wear a thumb brace
There are many types of thumb braces available. But overall, the main purpose is to
keep your thumb immobilized. This helps it heal from surgery, injury, or disease.
The most common reason to wear a thumb brace is either for a thumb sprain or
de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. However, other conditions might require a thumb brace such as:
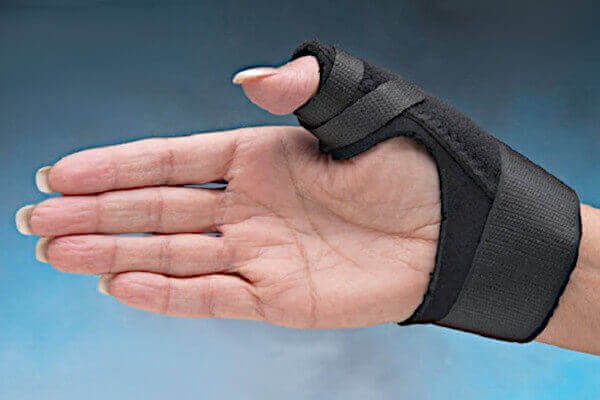
Does your thumb brace need a "spica"?
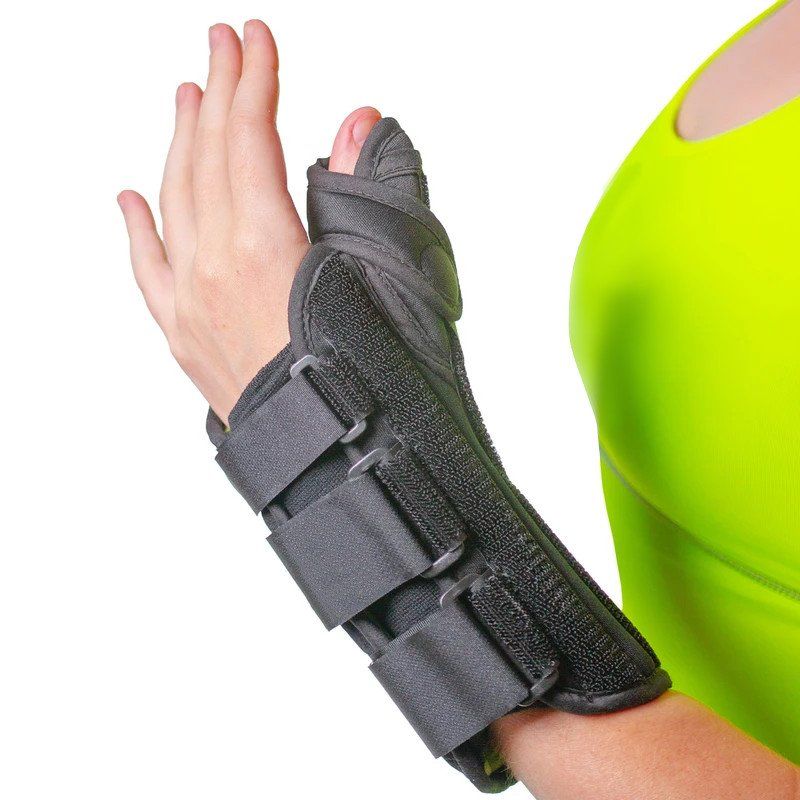
When movement restriction on the thumb is needed, the manufacturer adds a stiff "spica" to the brace. The spica is usually what distinguishes a "thumb brace" from a wrist brace.
The thumb spica is a rigid or semi-rigid extension of the hand brace that supports the thumb. It’s designed to keep the thumb stable and in one position.
Generally, thumb braces incorporate a spica for
post-surgical rehabilitation or as a substitute for a hand cast. Usually they include a simple Velcro-locked spica support or a lace-up spica.
Some thumb spicas are aluminum. But the vast majority of thumb spicas are lightweight
moldable plastic. That means you use a hairdryer to heat and bend the plastic spica to conform to the bend in your thumb. Usually your doctor's office will do this for you in order to ensure the best joint angles for maximum healing.
For the most part, good modern thumb braces with a spica will have this moldable plastic spine. But if your thumb does not require absolute immobility, a
fabric spica might be acceptable. Fabric spicas are semi-rigid.
Most important feature: COMFORT
You might need a thumb brace for post-surgical support or after a minor injury (like a sprain or partial ligament rupture). Either way, every patient, doctor, and manufacturer agrees that the best thumb brace feature to look for should be
comfort.
Good comfort allows tissues to heal better in the 3-6 weeks that most thumb injuries require. But far too many thumb braces are uncomfortable or even painful to wear. And that healing period can be maddening if the thumb brace is uncomfortable, causing you to squirm.
Such generic thumb braces are usually sold at Walmart, Walgreen's, and CVS. They're relatively inexpensive, but you may regret buying one after wearing it for a week.
Best thumb brace for
Sprains
You can sprain your thumb if you bend it too far, beyond its
normal range of motion. Too much bending will disrupt the ligaments that support the thumb. Beyond those physical limits, ligaments can develop micro-tears. As a result, inflammation and swelling follow. Severe thumb pain is the final outcome.
The most common thumb injuries occur in association with
contact sports like football or basketball. Some stick sports like hockey and lacrosse also contribute greatly to thumb injuries. The most severe cases require surgery to join completely ripped ligaments in the thumb. That's when a rigid thumb spica brace will better help keep the thumb from moving excessively.
It's also best to simultaneously immobilize the wrist joint. With severe thumb injuries, moving the wrist can be painful as well.
Therefore, a wrist brace with a thumb spica is best.
It's worth noting that many doctors recommend that ordinary (less severe) thumb sprains should
not
be kept completely rigid. Therefore, a fabric
semi-rigid thumb spica may be better. And again,
comfort is the primary concern here.
Best thumb brace for
de Quervain’s tenosynovitis
With simple diagnoses now available, doctors can easily
identify de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. It is essentially tendinitis at the base of the thumb. Usually it occurs in one of several ways, such as having arthritis or trauma to the thumb.
Also, repetitively and forcefully gripping and releasing objects (or tapping a phone) may be the culprit. This can produce thumb trauma and result in de Quervain's tenosynovitis.
If you have this condition, moving your thumb while grasping or making a fist will cause pain. In fact, it usually occurs in people who grip and release for prolonged periods of time (like hair stylists). The
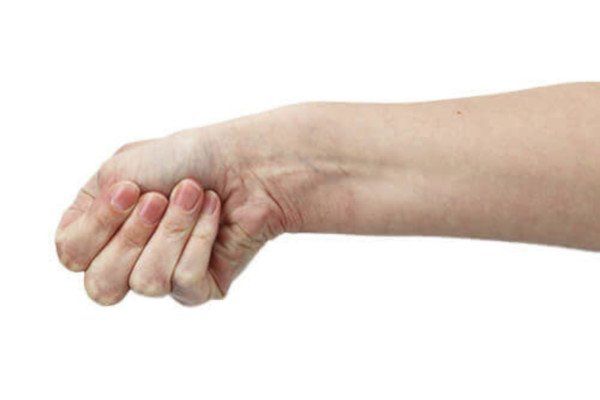
Finkelstein test can determine if you have de Quervain's.
Here's how the Finkelstein test is done. First, bend your thumb across your palm. Then close your fingers over your thumb. (You're making a fist with your thumb inside.) Now bend your wrist
toward your little finger. This will cause pain in your thumb (especially at its base) if you have de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
The most severe cases of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis require surgery. However, in the majority of instances the condition is treatable with cortisone injections, bracing, and 6 weeks of rest. Therefore, the 2 best thumb brace features to look for to treat de Quervain's tenosynovitis are a
rigid thumb spica and
comfort.
A rigid, comfortable thumb brace with a spica will help rest the thumb while the other fingers can work. Moreover,
for maximum benefit
wear the brace with spica day and night, generally for the entire 6 weeks.
If the de Quervain's tenosynovitis is severe, you might need additional wrist support as well. Immobilizing your wrist can help reduce pain. That means the best thumb brace will
also support your wrist.
Summary
A thumb brace is used when your thumb must be immobilized. Several conditions may require this. Therefore, the best thumb brace to look for will have a thumb spica. This will insure your thumb does not move during the therapy period. Of all the features to look for, a comfortable brace is paramount. Sometimes, when the disorder is severe, you may require a wrist brace that also contains a thumb spica.
FAQs
- Is it better to have a thumb spica anyway, even if I don't need it?
No, only use the thumb spica if you must keep your thumb immobilized.
- The Finkelstein test shows I have de Quervain's. What can be done?
You must see your doctor for treatment options.
This article explains more.
- Is it best to wear a brace 24/7?
It depends on your condition. Most disorders require constant wrist bracing. The notable exception is carpal tunnel syndrome. Then, you should brace only at night.
About