Why Are My Fingers Numb?
Table of Contents
- Overview
- What the Numbness Can Feel Like
- Primary Causes of Finger Numbness
1) Poor positioning
2) Stroke
3) Carpal tunnel syndrome
4) Cubital tunnel syndrome
5) Thoracic outlet syndrome
6) Diabetes
7) Vitamin B deficiency
8) Certain medicines
9) Cervical spondylosis
10) Raynaud's phenomenon
11) Alcohol-related neuropathy
- Other rarer disorders
- Summary
- FAQs
- About
Overview
If you’ve ever wondered, “Why are my fingers numb?” — you’re not alone. Finger numbness, whether it’s in your left hand, right hand, or both, is actually quite common. It can happen for many different reasons — from something as simple as a pinched nerve or vitamin deficiency to more serious conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or even a stroke.
When your fingers feel numb, it means you’re experiencing a partial or complete loss of sensation. Sometimes this happens just because you’ve put pressure on a nerve without realizing it — like when your hand “falls asleep.” In that case, the tingling or numbness usually fades once you move or change position.
However, if the numbness doesn’t go away or seems to be getting worse over time, it’s a sign that something deeper may be going on and that you should pay attention. The cause could be as mild as a
vitamin B deficiency (which is easy to treat) — or as serious as
carpal tunnel syndrome,
cervical spine problems, or even a warning sign of a
stroke.
Interestingly, numbness can appear in either hand with almost equal frequency. But if you have carpal tunnel syndrome, it tends to occur more often in your dominant hand — the one you use most for daily tasks.
No matter which hand is affected, numbness should never be ignored. Think of it as your body’s way of saying, “Something’s not right here.”
In this article, we’ll explore what finger numbness feels like, where it tends to occur, how long it lasts, and the most common conditions that cause it — along with other symptoms to watch for so you’ll know when to take action.
What the Numbness Can Feel Like
Finger numbness can feel differently from one person to another. But all numbness represents a type of
paresthesia. That means an abnormal sensation due to nerve injury.
The numb feeling means your skin is not as sensitive to touch. This abnormality is often accompanied by feelings described as:
- pins and needles
- prickling
- itching
- crawling bugs
- tickling
- burning
- falling asleep
- hot or cold skin
Primary Causes of Finger Numbness
1. Poor positioning
2. Stroke
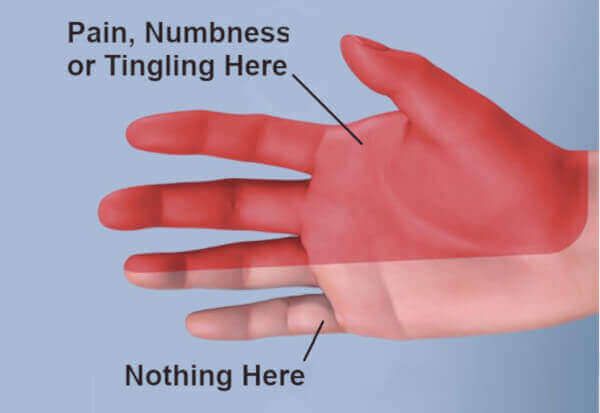
3. Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is usually attributed to overuse of your hands. That's why people in certain occupations are infamous for having this condition. They are:
Aside from "risky jobs", other
risk factors increase the probability of having carpal tunnel syndrome, These include being
pregnant, having
rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, wrist fracture, and being under
emotional stress.
It's important to understand which harmful finger and hand activities can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. They include prolonged gripping, wrist bending, and repetitive finger movements to name a few.
The entire list of harmful activities is found here.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated with 85-95% success using
non-surgical techniques. Occasionally,
carpal tunnel release surgery is needed, but the success rate is about 50%.
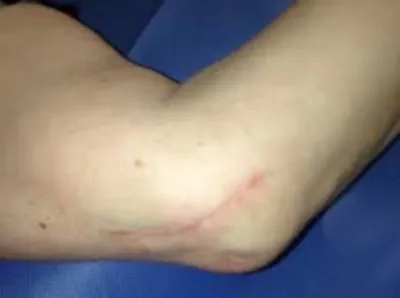
4. Cubital tunnel syndrome
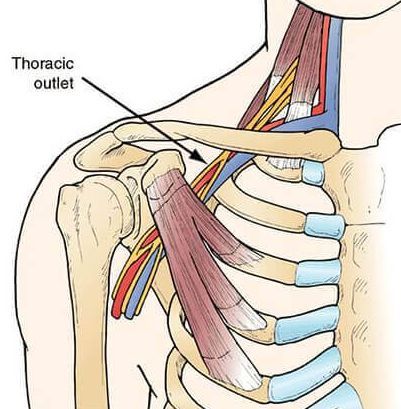
5. Thoracic outlet syndrome
Other symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome include:
- Weakened hand grip
- Cold arms, hand, and fingers
- Arm swelling
- Blue or pale color in the hand and fingers
You can tell if you have thoracic outlet syndrome by doing this
series of self-tests. A partner is required to help perform the tests.
Most instances of thoracic outlet syndrome can be treated non-surgically with
thoracic outlet syndrome exercises. More severe symptoms may require surgery to loosen the tissues from being compressed.
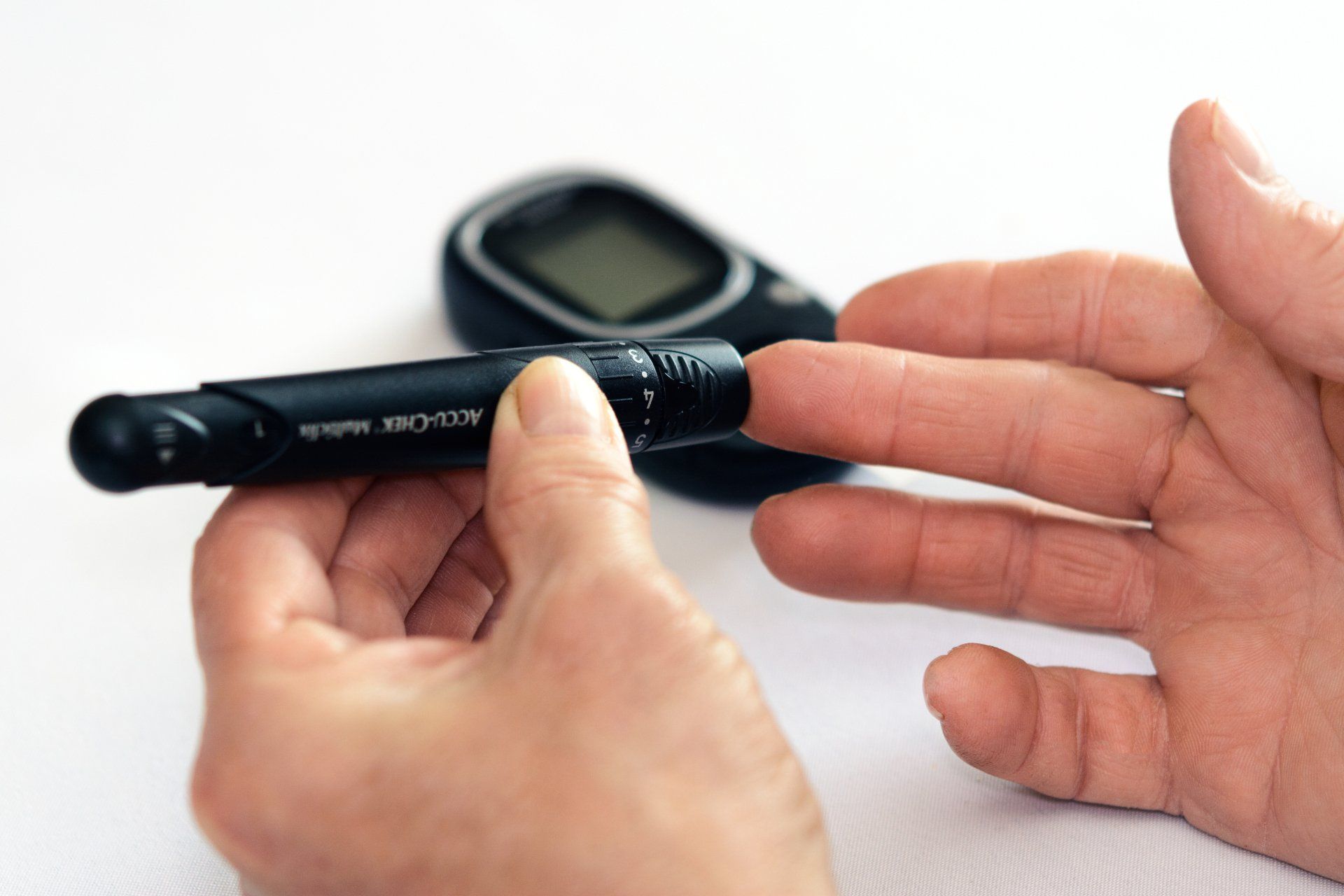
6. Diabetes
7. Vitamin B deficiency
8. Certain medicines
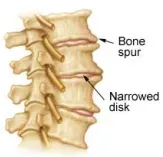
9. Cervical spondylosis
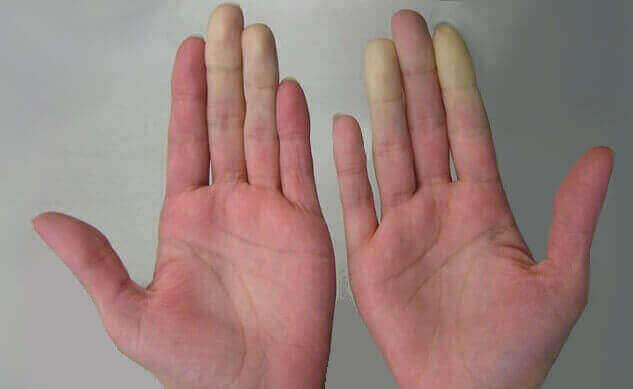
10. Raynaud's phenomenon
11. Alcohol-related neuropathy
Other rarer disorders
The following disorders are rarer than the ones listed above. However, they are known to cause hand or finger numbness. Left hand or right hand distinctions are not necessarily relevant.
Summary
There can be a number of reasons you have finger numbness. Numb fingers in your left or right hand generally is not as serious as numbness in both hands. Once you pinpoint which fingers are involved, you can determine which nerve is causing the numbness. Then, you can narrow down the possible candidate conditions and treat accordingly.
FAQs
Is it possible to have more than one finger numbing cause?
Yes. For instance, you can have diabetes and carpal tunnel syndrome simultaneously.
Does finger numbness definitely mean carpal tunnel?
No. Carpal tunnel syndrome can also appear as pain or tingling.
Of all these finger numbing conditions, which is the worst one to have?
Aside from the rarer disorders, most of the others are challenging to treat. However, oftentimes Raynaud's phenomenon is not treatable. Finger numbness due to poor sleeping position is the easiest to treat, and can be overcome in a week or two.
About