Can Too Much Sex Cause Carpal Tunnel?
Many people wonder if too much sex can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. It's actually not such a bizarre question. And it's certainly a topic worthy of serious discussion.
Your first response might be that the very idea is absurd. How can sexual intercourse and carpal tunnel possibly be related? But as it turns out, it's not so silly after all because
they can be related!
The relationship was first raised by
Dr. John Zenion. He studied the many risk factors for getting carpal tunnel syndrome. His study excluded
occupational risk factors like working with vibrating equipment, lifting heavy loads, etc. Of the 8 non-occupational risk factors, 4 could be attributed to changes in a person's frequency of having sexual intercourse. How that association is linked is outlined below.
How carpal tunnel syndrome happens
Before understanding how it's possible that too much sex causes carpal tunnel syndrome, let's discuss what this disorder is all about.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a type of
neuropathy. That means a nerve is injured or damaged. In this instance, we're specifically referring to the
median nerve in the wrist and hand.
The median nerve is one of the major nerves of the hand. Among other functions, it carries information to the brain like feelings like fine touch, pain, temperature, etc.
Wrist
flexor tendons also follow the same course as the median nerve; from the fingers, through the wrist joint, and up the forearm.
When tendons become stressed (by overworking them) they tend to inflame and swell. In the wrist, the swelling pushes against the median nerve. This pushing is what causes all of the
symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Eventually, and without treatment, the pushing and squeezing continues until you reach the
severe stage of the disorder.
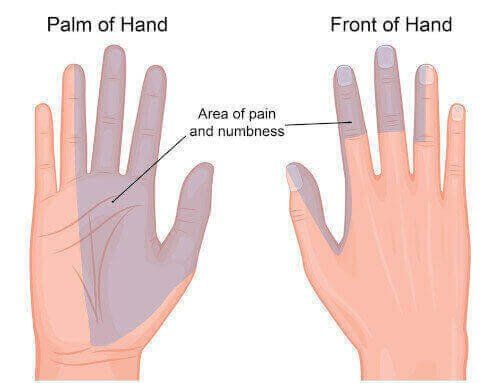
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
The symptoms of carpal tunnel occur in all of the fingers except the pinky finger. They also occur primarily on the palm side of the hand. The symptoms can vary from person to person, but generally include:
- Pain
- Numbness
- Pins & needles (tingling)
- Burning
- Soreness
- Weakness
- Itching
- Puffy feeling (without actual signs of swelling)
How sexual intercourse & carpal tunnel are related
The key is the bent hand
What does "too much sex" really mean? Most psychologists assert
there's no such thing, provided it involves a normal and healthy relationship.
And when it comes to physical exertion, sex is
relatively good exercise. In fact, men burn about 100 calories during sex. This compares to 276 calories burned on a treadmill.
But the evidence also suggests that when sexual intercourse is performed frequently, it increases the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. The
exact
reasons are unknown, Dr. Zenion suggests an indirect possibility: the relationship is likely due to excess pressure you exert on bent wrists during sex.
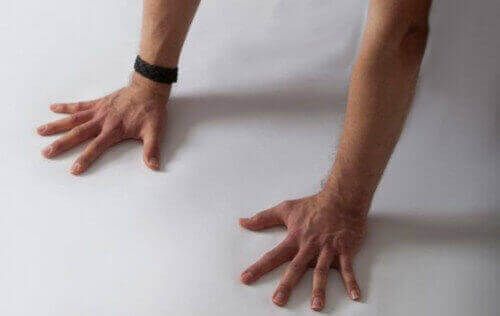
Bent hands increase internal wrist pressure
If a sexual participant is obese or has a large chest circumference, it produces a heavier upper body. So does the condition of macromastia. This is abnormal enlargement of the female breast tissue in excess of the person's normal proportion.
These conditions have the potential to produce excess pressure on bent wrists during sexual intercourse.
Certainly, the
bilateral nature of carpal tunnel syndrome can be easily explained this way. About
87% of people who have carpal tunnel syndrome in one hand will get symptoms in the other hand within 6 months.
Why? Perhaps because most normal humans use both hands to support the upper body during sexual intercourse. Dr. Zenion says that makes this association quite plausible.
In addition, the bent (extended) wrist joint is like a time bomb.
Hydrodynamic studies show that bending the wrist alone can increase the wrist's internal pressure 3-5 fold. So can bending just a couple fingers!
Now add to that pressure a person's upper body weight on the bent wrist during sexual intercourse. It's easy to see how that pressure can multiply several times.
Sex & carpal tunnel decline with age
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a problem of the median nerve being crushed by internal fluid pressure. It's only reasonable to assume that any added pressure (a bent wrist plus weight on the wrist) will add to the crushing force on the nerve.
Now consider the parallel between the incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome compared to the frequency of sexual intercourse during one's lifetime. Between the sixth and the seventh decades of life, the frequency of sexual intercourse
decreases over 6 fold (combining male and female data).
Interestingly, the probability of getting carpal tunnel syndrome during that same age range
falls 4-5 fold. Is this just a coincidence? Perhaps.
But while there might not be a
direct
correlation, it certainly is curious that the incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome is proportional to the decline in sexual intercourse with age. Of course, other factors like some morbidities (which can lead to increased carpal tunnel risk) in addition to decreased libido (resulting in less frequent sex) may play a role.
How to treat carpal tunnel syndrome
Nocturnal bracing
Rest and avoid excessive hand strain
Stretching exercises
Massage (using myofascial release)
Conclusion
Can too much sex cause carpal tunnel syndrome? Nobody knows for sure. However, assuming sexual activity involves exerting high stresses on the wrist joints, then good evidence suggests that frequent sexual activity will overly stress your wrists. By extension, therefore, sexual frequency should have an impact on the probability of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Additional factors such as obesity may exacerbate stresses on the wrist during sex. Obviously, this theoretical relationship requires more validation.